A Scheduling Optimization Method of Shared Bicycles Based on a Multi-objective Ant Colony Algorithm
-
摘要: 共享单车作为公共交通接驳、“最后一公里”出行的重要交通工具,存在供需时空不匹配的问题,需要利用调度车实现共享单车的再平衡。针对部分现有共享单车调度方法存在的优化目标单一、调度点只能被访问1次、未考虑连续调度衔接等问题,建立了以总需求不满足度最小和调度成本最小为目标的多目标优化模型。该模型考虑高峰小时调度点需求远大于调度车容量的情况,允许多辆调度车多时段连续调度,且允许调度车重复访问调度点。设计了多目标蚁群算法进行求解,引入非支配排序方法,将解集划分为不同的非支配层级,取最高层级的解,形成1组同时考虑2个目标的Pareto最优解。该算法引入了最大-最小蚂蚁系统,改进了状态转移概率规则和信息素更新规则,使其能够适用于求解多目标优化问题。算例结果表明,该模型能够在保证较低调度成本的同时,减少需求损失,算例调度后的总需求不满足度由不进行调度时的26.48%降低到17.86%。将不同算例规模下多目标蚁群算法与贪心算法求解结果进行比较,多目标蚁群算法在多时段连续调度问题上具有优势,能够统筹安排每辆调度车在每个调度周期的行驶路径和在各调度点的到达时间和共享单车装卸数量。多目标蚁群算法所求得的解的质量优于贪心算法,较大规模算例求解得到的调度成本和总需求不满足度比贪心算法分别降低了62%和23%。Abstract: As a crucial mode for facilitating public transportation connections and addressing the "last mile" problem, shared bicycles confront the challenge of supply and demand imbalances. To solve this issue, deploying vehicles for scheduling purposes becomes an essential step in rebalancing the shared bicycles. In order to address the issues of current shared bicycle scheduling methods including single optimization objective, limited visits to scheduling sites, and insufficient consideration of continuous scheduling connections, a multi-objective optimization model is developed in this paper to minimize both total demand dissatisfaction and scheduling costs. This model considers the situation that the demand at the scheduling site surpasses the capacity of the scheduling vehicle during peak hours. Consequently, it enables the scheduling vehicle to make multiple trips to the site and allows to conduct continuous scheduling in multiple periods of time for multiple vehicles. A multi-objective ant colony algorithm is designed to solve this model by integrating the technique of non-dominated sorting to classify the solution set into various levels of non-dominance. The solution at the highest level is then utilized to create a Pareto-optimal solution, which considers two objectives concurrently. This algorithm introduces a new ant system incorporating maximum-minimum criteria, modifies the state transition probability rule and pheromone update rule to enhance their efficacy to deal with the multi-objective optimization problem. In order to verify the feasibility of the model and algorithm, a case study is carried out. The results show that the model is confirmed to be effective in decreasing demand loss while ensuring the lower scheduling costs. Specifically, the total demand dissatisfaction degree is reduced from 26.48% to 17.86%. Comparing the results of the multi-objective ant colony algorithm and greedy algorithm under various example sizes, the multi-objective ant colony algorithm shows a clear superiority in continuous scheduling of multiple periods of time. Specifically, it is capable of organizing the driving path of each scheduling vehicle in each scheduling cycle, as well as the arrival time and the loading and unloading numbers of shared bicycles at each scheduling site. Meanwhile, compared with greedy algorithm, the multi-objective ant colony algorithm shows a clear superiority in the quality of the solutions, and the scheduling costs and total demand dissatisfaction degree obtained in a large-scale case are reduced by 62% and 23%, respectively.
-
表 1 相关文献对比
Table 1. Comparison of relevant literature
研究者 静态/动态调度 目标函数 求解算法 是否是多目标优化 是否允许多次访问调度点 多时段调度 Raviv等[3] 静态 总调度成本最小、总惩罚成本最小 启发式算法 否 是 是 Erdoğan[4] 静态 路线总成本最小 分离算法 否 是 否 蒋塬锐等[5] 静态 调度总成本最小 遗传算法 否 是 否 关宏志等[6] 静态 调度时间成本最小 求解器 否 否 否 于德新[14] 静态 成本最小、投放率最高 改进遗传算法 是 否 否 曾琼燕等[9] 动态 总利润最大 模拟退火算法 否 否 是 Zhang[10] 动态 车辆出行成本最小、用户不满足度最小 启发式算法 否 否 是 Hu等[11] 动态 整体满意度利润最小、再平衡成本最小 MOEA/D 是 否 是 汪慎文等[19] 动态 调度量最大 改进蚁群算法 否 是 否 本文 动态 调度成本最小、总需求不满足度最小 多目标蚁群算法 是 是 是 表 2 模型符号含义
Table 2. Model symbolic meaning
符号 含义 集合 V 调度点集合 K 调度车集合 索引 i 调度点索引,i ∈ V j 调度点索引,j ∈ V k 调度车索引,k ∈ K t 调度周期索引,将调度计划期划分为m个调度周期,t = 1,2,…,m 参数 T 调度周期的时间长度 C 调度车容量 lij 从调度点i到调度点j的距离 Ii(t) 调度点i在周期t的骑入量 Oi(t) 调度点i在周期t的需求满足量 v 车辆速度 g 共享单车的单位装卸时间 w 单位距离成本 决策变量 xijk(t) 二元变量,如果xijk(t) = 1,则车辆k在周期t从调度点i行驶到调度点j,否则为0 yijk(t) 当车辆k在周期t从调度点i行驶到调度点j时,车辆k上携带的共享单车数量。如果车辆k不从i行驶到j,则yijk(t) 为零 zik(t) 车辆k在周期t在调度点i的共享单车装卸数量,zik(t) < 0表示卸车,zik(t) > 0表示装车 辅助变量 Si(t) 调度点i在周期t的初始供给量 di(t) 调度点i在周期t的需求量 表 3 调度中心位置
Table 3. Scheduling center location
调度中心 经度/(°) 纬度/(°) 0 116.534 107 39.974 810 表 4 调度点位置和需求
Table 4. Scheduling site location and requirements
调度点 经度/(°) 纬度/(°) 初始存量/辆 周期1 周期2 周期3 周期4 骑入量/辆 需求量/辆 骑入量/辆 需求量/辆 骑入量/辆 需求量/辆 骑入量/辆 需求量/辆 1 116.534 107 39.974 810 200 531 668 657 833 417 367 758 611 2 116.534 568 39.974 349 100 27 91 30 101 50 13 100 39 3 116.539 664 39.973 239 80 18 50 20 56 36 15 73 25 4 116.539 364 39.977 137 10 20 15 43 16 8 25 15 60 5 116.543 248 39.974 374 65 20 66 22 74 20 40 96 29 6 116.544 986 39.976 873 5 30 11 33 12 7 20 13 52 7 116.544 342 39.971 858 5 25 9 27 10 7 30 13 40 8 116.548 559 39.976 018 5 49 18 55 20 20 20 30 71 9 116.548 119 39.973 626 5 40 16 45 18 12 50 23 58 10 116.547 883 39.971 455 80 33 96 36 107 8 20 139 47 11 116.548 955 39.980 639 45 29 65 32 72 20 40 94 42 12 116.550 758 39.978 156 5 71 40 79 44 23 62 45 103 13 116.552 174 39.973 034 76 26 88 29 98 64 10 127 38 14 116.552 314 39.974 859 5 56 55 71 61 10 70 70 92 15 116.554 674 39.977 934 5 80 76 100 80 49 78 100 130 16 116.554 551 39.973 490 25 8 19 8 21 14 35 27 11 17 116.558 569 39.971 348 50 899 722 1 108 896 433 656 865 1 048 18 116.556 938 39.975 352 50 9 28 9 32 30 9 50 12 19 116.558 815 39.977 613 16 18 28 20 28 10 28 20 30 20 116.558 976 39.980 351 57 11 34 12 37 30 8 50 16 21 116.561 648 39.978 748 5 85 27 95 30 18 86 30 123 22 116.560 865 39.982 875 70 16 46 18 51 36 5 60 23 表 5 各周期调度车的调度路径、装卸量和到达时间
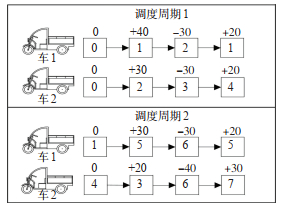
Table 5. The scheduling route, loading and unloading volume and arrival time of the scheduling vehicles in each cycle
车辆编号 周期1 周期2 周期3 路径 装卸车数量/辆 到达时间/s 路径 装卸车数量/辆 到达时间/s 路径 装卸车数量/辆 到达时间/s 车辆1 0 0 0 8 4 0 6 -37 0 3 12 76 9 -11 155 2 37 1 173 4 15 530 8 11 520 4 -40 2 340 5 -27 1 026 11 -20 941 7 21 1 889 5 -20 1 620 11 -21 2 576 4 10 2 266 8 36 3 297 6 30 2 623 车辆2 0 0 0 13 0 0 19 -10 0 9 29 182 17 30 58 18 28 344 13 -29 1 144 14 -40 1 025 17 -37 1 238 12 36 2 045 17 40 2 292 13 37 2 406 13 -26 3 156 19 -18 3 590 12 -40 3 547 表 6 不同算例规模下2种算法求解结果比较
Table 6. Comparison of results between two algorithms under different example sizes
指标 算例22 算例36 多目标蚁群算法 贪心算法 多目标蚁群算法 贪心算法 目标函数 14.82 22.58 16.19 31.09 调度成本/元 11.67 25.40 14.92 39.51 总需求不满足度/% 17.96 19.76 17.46 22.67 运行时间/s 81.00 0.13 213.67 0.42 -
[1] WANG Z L, CHEN F, XU T K. Interchange between metro and other modes: access distance and catchment area[J]. Journal of Urban Planning and Development, 2016, 142(4): 04016012. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)UP.1943-5444.0000330 [2] 尹芹, 孟斌, 张丽英. 基于客流特征的北京地铁站点类型识别[J]. 地理科学进展, 2016, 35(1): 126-134.YIN Q, MENG B, ZHANG L Y. Classification of subway stations in Beijing based on passenger flow characteristics[J]. Progress in Geography, 2016, 35(1): 126-134. (in Chinese) [3] RAVIV T, TZUR M, FORMA I A. Static repositioning in a bike-sharing system: models and solution approaches[J]. EURO Journal on Transportation and Logistics, 2013, 2(3): 187-229. doi: 10.1007/s13676-012-0017-6 [4] ERDOĞAN G, BATTARRA M, CALVO R W. An exact algorithm for the static rebalancing problem arising in bicycle sharing systems[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2015, 245(3): 667-679. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2015.03.043 [5] 蒋塬锐, 贾顺平, 李军. 基于调度池的共享单车调度研究[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2019, 37(5): 124-132. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1674-4861.2019.05.016JIANG Y R, JIA S P, LI J. A study of bicycle-sharing scheduling based on scheduling pool[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2019, 37(5): 124-132. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1674-4861.2019.05.016 [6] 关宏志, 卢笙, 宋茂灿. 共享单车分层调度策略研究[J]. 重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 39(2): 1-7.GUAN H Z, LU S, SONG M C. Hierarchical scheduling strategy for free-floating bike-sharing[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science), 2020, 39(2): 1-7. (in Chinese) [7] 高楹, 宋辞, 舒华, 等. 北京市摩拜共享单车源汇时空特征分析及空间调度[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2018, 20(8): 1123-1138.GAO Y, SONG C, SHU H, et al. Spatial-temporal characteristics of source and sink points of mobikes in Beijing and its scheduling strategy[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 2018, 20(8): 1123-1138. (in Chinese) [8] 谢青成, 毛嘉莉, 刘婷. 城市共享单车的动态调度策略[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, (6): 88-102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5641.2019.06.009XIE Q C, MAO J L, LIU T. Dynamic scheduling strategy for bicycle-sharing in cities[J]. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), 2019, (6): 88-102. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5641.2019.06.009 [9] 曾琼燕, 杨晟. 基于模拟退火算法的共享单车动态调度问题研究[J]. 综合运输, 2023, 45(2): 75-79.ZENG Q, YANG S. Dynamic scheduling of shared bicycles based on simulated annealing algorithm[J]. China Transportation Review, 2023, 45(2): 75-79. (in Chinese) [10] ZHANG D, YU C, DESAI J, et al. A time-space network flow approach to dynamic repositioning in bicycle sharing systems[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2017, 103: 188-207. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2016.12.006 [11] HU R, ZHANG Z, MA X, et al. Dynamic rebalancing optimization for bike-sharing system using priority-based MOEA/D algorithm[J]. IEEEAccess, 2021, 9: 27067-27084. [12] SHUI C S, SZETO W Y. Dynamic green bike repositioning problem-a hybrid rolling horizon artificial bee colony algorithm approach[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2018, 60: 119-136. [13] PAL A, ZHANG Y. Free-floating bike sharing: Solving real-life large-scale static rebalancing problems[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2017, 80: 92-116. [14] 于德新, 张行, 王薇, 等. 共享单车调度模型及算法研究[J]. 重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 39(7): 1-7.YU D X, ZHANG H, WANG W, et al. Scheduling model and algorithm for shared bicycle[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science), 2020, 39(7): 1-7. (in Chinese) [15] 孙卓, 李一鸣. 考虑多仓库的共享单车重新配置问题研究[J]. 运筹与管理, 2021, 30(1): 121-129.SUN Z, LI Y M. Solving a static bike repositioning problem with multiple depots[J]. Operations Research and Management Science, 2021, 30(1): 121-129. (in Chinese) [16] 徐国勋, 张伟亮, 李妍峰. 共享单车调配路线优化问题研究[J]. 工业工程与管理, 2019, 24(1): 80-86.XU G X, ZHANG W L, LI Y F. Research on optimization of shared bicycle repositioning routing problem[J]. Industrial Engineering and Management, 2019, 24(1): 80-86. (in Chinese) [17] SHI L, ZHANG Y, RUI W N, et al. Study on the bike-sharing inventory rebalancing and vehicle routing for bike-sharing system[J]. Transportation Research Procedia, 2019, 39: 624-633. [18] CAGGIANI L, CAMPOREALE R, OTTOMANELLI M, et al. A modeling framework for the dynamic management of free-floating bike-sharing systems[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2018, 87: 159-182. [19] 汪慎文, 徐亮, 杨锋, 等. 基于蚁群算法的动态共享单车调度优化[J]. 南昌工程学院学报, 2019, 38(3): 71-76.WANG S W, XU L, YANG F, et al. Optimization of dynamic shared bike scheduling based on ant colony[J]. Journal of Nanchang Institute of Technology, 2019, 38(3): 71-76. (in Chinese) [20] ZHAO B L, GUI H X, LI H Z, et al. Cold chain logistics path optimization via improved multi-objective ant colony algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, (8): 142977-142995. -





 下载:
下载: