A Geometric Information Extraction Method of Road Signs in LiDAR Point Cloud Based on RPCA
-
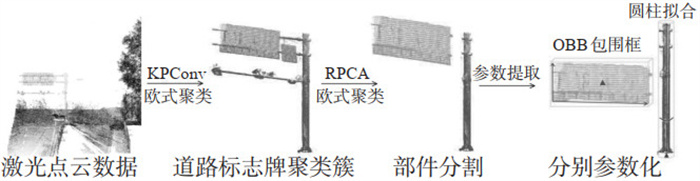
摘要: 道路标牌的位置、尺寸等几何参数普查是交通资产管理、无人驾驶等应用的关键环节。车载激光扫描三维点云中路牌不仅占比小,而且受周围树木干扰大,导致边缘点云缺失且包含大量噪声。为了准确提取点云中标牌杆和平面的位置和几何信息,提出了两阶段杆状物点云分割方法,由粗及细提取出标牌杆及其相连的标牌平面点云簇;进而通过鲁棒主成分分析(robust principal component analysis,RPCA)排除标牌周围噪声和杂点干扰,结合点云簇形态分析得到独立的主杆体和标牌平面2个部件;再引入环状域生长拟合圆柱体,法向量投影采样与定向包围盒(oriented bounding box,OBB)紧致拟合标牌平面,分别得到主杆体和标牌的准确几何信息。实验采集了湖北省武汉市洪山区、高新区和武昌区34个不同路口下的激光点云数据,在KPConv点云分割网络下进行训练与验证,准确率达到90.31%,标牌精确度达到91.07%,召回率达到了92.74%;并对上述数据中的20个路口的98个道路标牌进行几何信息提取,有效提取率达到89.80%,位置精度达到0.062 1 m,几何误差达到8.07%。实验表明:该方法能有效排除点云噪声和杂点干扰,实现对点云缺失在20%以内的标牌的有效提取。Abstract: The extraction of geometric parameters of road signs, such as position and sizes, is a crucial aspect of transportation asset management and autonomous driving applications. In vehicular LiDAR point clouds, road signs occupy a small proportion, and are subject to significant interference from surrounding trees, resulting in blurred edges and noise. To accurately extracting the geometric information of road signs, a two-stage pole-like object point cloud segmentation method is proposed. Subsequently, robust principal component analysis (RPCA) is employed to eliminate noise and extraneous points around the signs. The components of independent central poles and sign planes are obtained through the shape analysis of point cloud clusters. Finally, introduce the annular region growth to fit the central poles, and employ normal vector projective sampling and oriented bounding box (OBB) to approxi-mate the signs. Thus, accurate geometric information is obtained for both the central pole and the sign. Experiments are conducted using laser point cloud from 34 different intersections in the Hongshan, Gaoxin, and Wuchang dis-tricts of Wuhan, China. Training and validation using the KPConv segmentation network achieves an accuracy of 90.31%, a precision of 91.07%, and 92.74% recall rate. Additionally, the extraction of geometric information is con-ducted on 98 road signs from 20 intersections within the data above. This method achieves an effective extraction rate of 89.80%, a positional accuracy of 0.062 1 m, and 8.07% geometric error. The experiments demonstrate that this method effectively eliminates noise and extraneous point interference, and performs well on those signs with missing point clouds within 20%.
-
表 1 几何信息提取数据集中标牌形态分布
Table 1. Morphological distribution of road signs in the dataset
数据集 路口数 方形标牌数 圆形标牌数 标牌总数 武昌区 6 14 6 20 八一路 5 18 8 26 高新区 9 31 21 52 总计 20 63 35 98 表 2 标牌提取运行环境
Table 2. Operating environment of sign extraction
项目 型号 CPU 12th Gen Intel Core i5-12490F GPU NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4060Ti 16GB 操作系统 Ubuntu 22.04 Python 3.8 CUDA 11.6 cudnn 8.9.6 Pytorch 1.13.1 表 3 混淆矩阵中的样例预测组合
Table 3. Sample predictions in the confusion matrix
真实类型 预测类型 背景点 杆状物 树木 背景点 A B C 杆状物 D E F 树木 G H I 表 4 测试集下KPConv与AGConv的精度指标对比
Table 4. Evaluation of KPConv and AGConv on test set
分割网络 准确度/% 精度/% 召回率/% 标牌 树木 标牌 树木 KPConv 90.31 91.07 81.50 92.74 99.26 AGConv 90.34 77.54 82.39 95.57 98.67 表 5 道路标牌几何信息提取效果
Table 5. Geometric information extraction effect of road signs
采集区域 路口数标牌数 位置精度/m 几何误差/% 有效提取率/% 总用时/s 八一路1 2 9 0.082 3 10.91 88.89 1 016 八一路2 3 17 0.072 1 10.20 88.23 4 284 武昌区 6 20 0.053 4 6.31 90.00 5 179 高新区 9 52 0.057 5 7.57 90.38 22 594 汇总 20 98 0.062 1 8.07 89.80 33 073 表 6 道路标牌几何信息提取有效提取率对比
Table 6. Comparison of the effective extraction rate in geometric information extraction of road signs
表 7 点云缺失下道路标牌几何信息提取效果
Table 7. Geometric information extraction effect of road signs based on defective point cloud
缺失程度 数据示例 精度 完整 
位置精度/m 0.046 1 几何误差/% 4.70 约5% 
位置精度/m 0.059 5 几何误差/% 7.39 约10% 
位置精度/m 0.082 1 几何误差/% 11.07 约20% 
位置精度/m 0.096 4 几何误差/% 15.80 30%以上 
位置精度/m 0.132 6 几何误差/% 21.51 -
[1] MATTHEW V, MEDHAT M. Deep learning for intelligent transportation systems: a survey of emerging trends[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems. 2020, 21(8): 3152-3168. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2019.2929020 [2] 林述涛. 面向多源数据融合的交通基础设施数字化架构研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2018, 35(9): 122-127, 145. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLJK201809018.htmLIN S T. Study on digital architecture of transportation infrastructure for multi-source data fusion[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development. 2018, 35(9): 122-127, 145. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLJK201809018.htm [3] HUANG P D, CHENG M, CHEN Y P, et al. Traffic sign occlusion detection using mobile laser scanning point clouds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 18(9): 2364-2376. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2016.2639582 [4] GARGOUM S, El-BASYOUNY K, SABBAGH J, et al. Automated highway sign extraction using lidar data[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2017, 2643(1): 1-8. doi: 10.3141/2643-01 [5] 黄明, 车平文, 韦朋成. 道路点云中交通标志牌的识别提取研究[J]. 测绘科学, 2023, 48(2): 115-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHKD202302015.htmHUANG M, CHE P W, WEI P C. Research on recognition and extraction of traffic signs in road point cloud[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2023, 48(2): 115-123. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHKD202302015.htm [6] GARGOUM S, El-BASYOUNY K. Automated extraction of road features using LiDAR data: a review of LiDAR applications in transportation[C]. 4th International Conference on Transportation Information and Safety(ICTIS). Banff, Canada: IEEE, 2017. [7] 瓮升霞, 陈一平. 基于移动激光点云的交通标志牌特征提取[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 55(4): 580-585. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDZK201604023.htmWENG S X, CHEN Y P. Road-traffic-sign detection from mobile LiDAR point clouds[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 2016, 55(4): 580-585. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDZK201604023.htm [8] JAVANMARDI M, SONG Z, QI X. Automated traffic sign and light pole detection in mobile LiDAR scanning data[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2019, 13(5): 803-815. doi: 10.1049/iet-its.2018.5360 [9] YANG B S, DONG Z, ZHAO G, et al. Hierarchical extraction of urban objects from mobile laser scanning data[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2015, 99: 45-57. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2014.10.005 [10] PLACHETKA C, FRICKE J, KLINGNER M, et al. DNN-based recognition of pole-like objects in LiDAR point clouds[C]. 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference(ITSC). Indianapolis, The United States of America: IEEE, 2021. [11] PARK J, KIM C, KIM S, et al. PCSCNet: Fast 3D semantic segmentation of LiDAR point cloud for autonomous car using point convolution and sparse convolution network[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2023, 212: 118815. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.118815 [12] CELESTINO O, CARLOS C, ENOC S-A. Automatic detection and classification of pole-like objects for urban cartography using mobile laser scanning data[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(7): 1465. doi: 10.3390/s17071465 [13] HUANG P D, CHEN Y P, LI J, et al. Extraction of street trees from mobile laser scanning point clouds based on subdivided dimensional features[C]. 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium(IGARSS). Milan, Italy: IEEE, 2015. [14] TRUONG-HONG L, LINDENBERGH R C, VERMEIJ M J. Efficient sparse street furniture extraction from mobile laser scanning point clouds[J]. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2022, 48(4): 161-168. [15] WEN C L, LI J, LUO H, et al. Spatial-related traffic sign inspection for inventory purposes using mobile laser scanning data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2015, 17(1): 27-37. [16] 朱云涛, 李飞, 胡钊政, 等. 基于3D点云语义地图表征的智能车定位[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2021, 39(6): 143-152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JTJS202106017.htmZHU Y T, LI F, HU Z Z, et al. A localization method for intelligent vehicles based on semantic map representation extracted from 3D cloud points[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2021, 39(6): 143-152. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JTJS202106017.htm [17] THOMAS H, QI C R, DESCHAUD J E, et al. KPConv: flexible and deformable convolution for point clouds[C]. the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, Korea: IEEE, 2019. [18] CAND S E J, LI X, MA Y, et al. Robust principal component analysis[J]. Journal of the ACM (JACM), 2011, 58(3): 1-37. [19] WEI M Q, WEI Z Y, ZHOU H R, et al. Agconv: Adaptive graph convolution on 3d point clouds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(8): 9374 - 9392. [20] HUANG Y C, MA P, JI Z, et al. Part-based modeling of pole-like objects using divergence-incorporated 3-D clustering of mobile laser scanning point clouds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 59(3): 2611-2626. [21] HE S W, LIU B l. Review of bounding box algorithm based on 3D point cloud[J]. International Journal of Advanced Network, Monitoring and Controls, 2021, 6(1): 18-23. -





 下载:
下载: